Terms and definitions
The solar energy transmission factor
The solar energy reflection factor
The low-emission coating
The low-emission coating: The coating that improves thermotechnical properties of the glass (increasing resistance to heat transfer of glazing with application of low-emission coating glass, decreasing the ratio of heat transfer).
The solar protective coating
The solar protective coating: The coating applied to glass enhances room’s protection against excessive sun radiation penetration.
The emission factor
The emission factor (corrected emission factor): the relation of the rate of emission of glass’s surface to the rate of emission of a black body.
The normal emission factor
The normal emission factor (normal ability of emission): The ability of glass to reflect normally incoming radiation is calculated as a difference between one and the normal reflection factor towards glass’s surface.
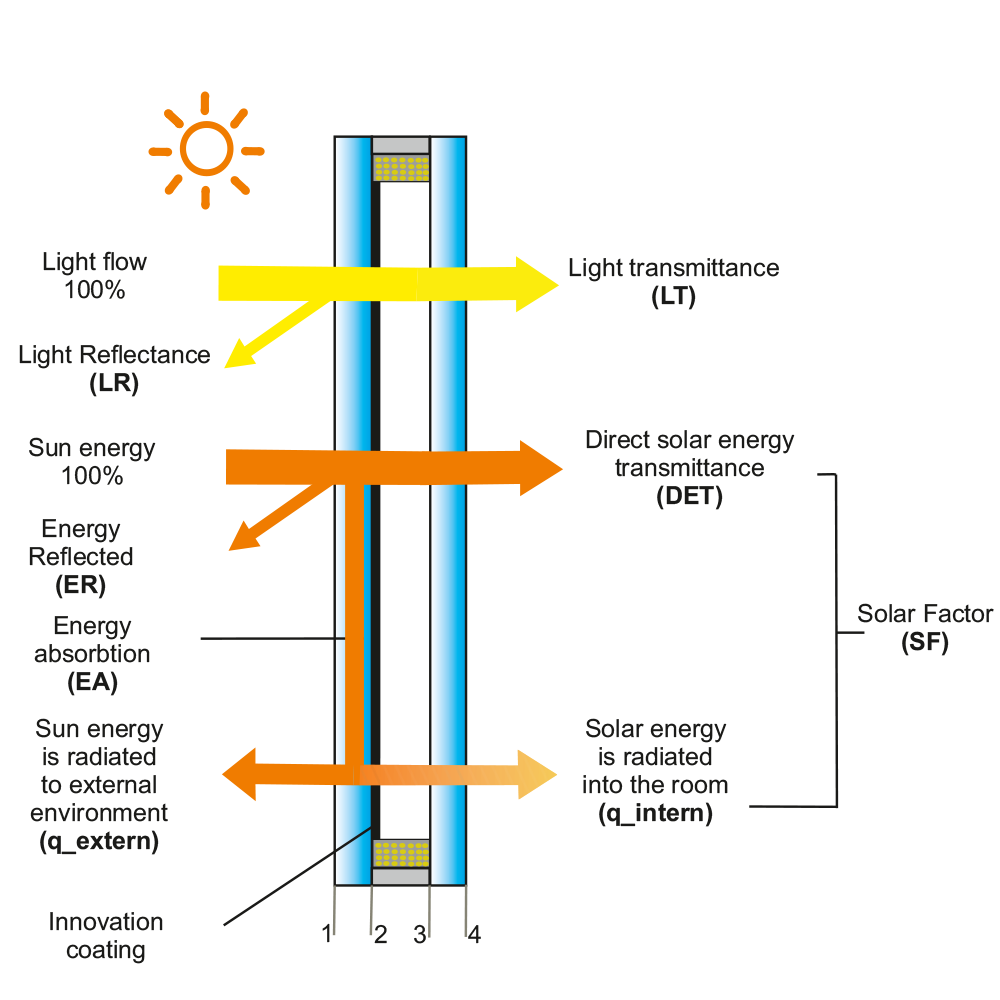
The solar factor
The solar factor (aggregate solar energy transmission factor): the relation of aggregate incoming solar energy going through transparent construction to incoming solar radiation energy. Aggregate incoming solar energy going through the transparent construction is an amount of energy directly going through transparent construction and absorbed via the transparent construction energy that is transferred inside.
The regular light transmission factor
The regular light transmission factor (identical terms: light transmission factor, light transmission coefficient), is denoted by τv (LT) – the relation of the value of light flow normally gone through the sample to value of the light flow that normally falls upon the sample (within the range of visible light waves).
The light reflection factor
The light reflection factor (identical term: normal light reflection coefficient) is denoted as ρv (LR) – the relation of the value of light flow normally reflected from the sample to the value of light flow normally falling upon the sample (within the range of visible light waves).
The light absorption factor
The light absorption factor is denoted as av (LA) – the relation of the value of light flow absorbed by the sample to the value of light flow normally falling upon the sample (within the range of visible light waves).
The solar energy transmission factor
The solar energy transmission factor (identical term: direct solar energy transmission factor) is denoted as τe (DET) – the relation of the value of solar radiation flow normally gone through the sample to the value of solar energy radiation normally falling upon the sample.
The solar energy reflection factor
The solar energy reflection factor is denoted as pe (ER) – the relation of the value of solar radiation flow normally reflected from the sample to the value of solar radiation flow normally falling upon the sample.
The solar energy absorption factor
The solar energy absorption factor (identical term: energy absorption factor) is denoted as ae (EA) – the relation of the value of solar radiation flow absorbed by the sample to the value of solar radiation flow normally falling upon the sample.
The shading coefficient
The shading coefficient is denoted as SC or G – the shading factor is the relation of solar radiation flow going through the given glass within the wave range 300 dog 2500 nm (2.5 mcm) to solar energy flow gone through the glass, 3mm thickness. The shading factor shows a ratio of transmission of both direct solar energy flow and (the near-infrared radiation) and radiation due to energy absorbed in the glass (far infrared radiation).
The heat transfer factor
The heat transfer factor is denoted as U, and measured amount of heat in Watts (W), that goes through 1 m2 of the construction with the difference between inward and outward temperatures amounting to 1 degree Kelvin (K), unit of measure W/(m2•K).
Heat transfer resistance
Heat transfer resistance is denoted as R and is reciprocal to the heat transfer factor.
How does the glass